Power Generators: Understanding Types, Benefits, and Applications
Power generators are essential devices that provide electricity in various settings, from emergency backup to remote locations without grid access. These machines convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, ensuring a reliable power supply when needed most. This article explores different types of power generators, their applications, and key considerations for selecting the right one for your needs.

What are the main types of power generators?
Power generators come in several types, each suited for different purposes and environments:
-
Gasoline Generators: These are common for residential use and small businesses. They’re portable and relatively inexpensive but have limited run times and require frequent refueling.
-
Diesel Generators: Known for their durability and efficiency, diesel generators are often used in industrial settings and for large-scale backup power. They have longer run times than gasoline generators but can be noisier and more expensive upfront.
-
Natural Gas Generators: These generators connect directly to natural gas lines, providing extended run times without the need for refueling. They’re cleaner-burning than diesel or gasoline but require a fixed installation.
-
Propane Generators: Similar to natural gas generators, propane models offer clean-burning operation and can be portable or stationary. They’re often used in areas where natural gas isn’t available.
-
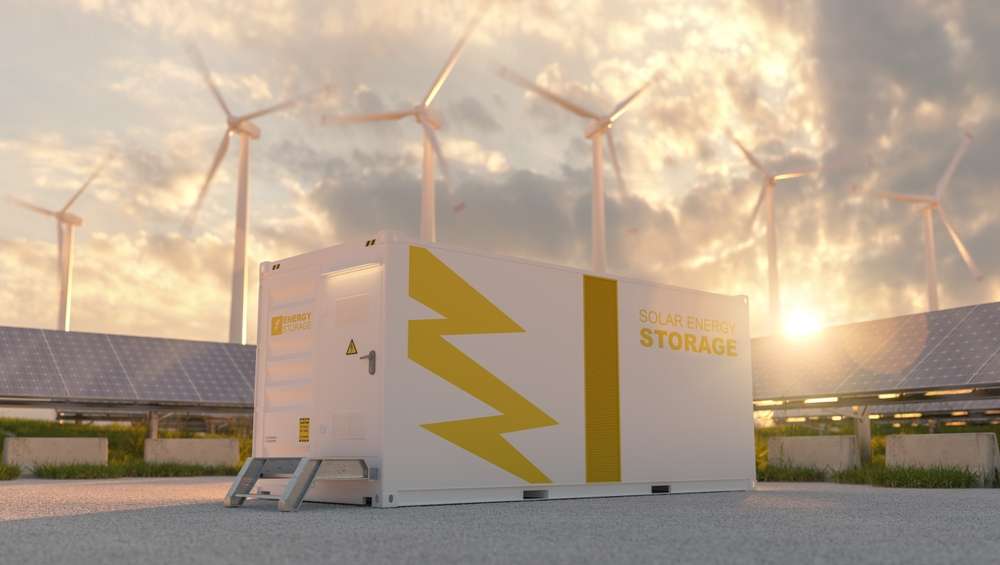
Solar Power Generators: These environmentally friendly options use solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity, storing it in batteries for later use. They’re silent and have no fuel costs but depend on weather conditions and may have limited power output.
How do solar power generators work?
Solar power generators harness energy from the sun using photovoltaic panels. These panels contain cells that convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. The process involves several components:
-
Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it to DC electricity.
-
Charge Controller: Regulates the flow of electricity to prevent overcharging the battery.
-
Battery: Stores the generated electricity for later use.
-
Inverter: Converts DC power from the battery into AC power for use with standard appliances and devices.
Solar power generators are becoming increasingly popular due to their eco-friendly nature and ability to provide off-grid power. They’re particularly useful for camping, RVs, and as backup power sources for homes in sunny climates.
What factors should be considered when choosing a power generator?
Selecting the right power generator depends on several factors:
-
Power Requirements: Calculate the total wattage needed to run essential appliances and devices simultaneously.
-
Fuel Type: Consider availability, cost, and storage of different fuel types in your area.
-
Portability: Determine if you need a stationary or portable generator based on intended use.
-
Noise Level: Some generators can be quite loud, which may be a concern in residential areas or camping sites.
-
Runtime: Consider how long the generator needs to operate without refueling or recharging.
-
Maintenance: Factor in the ongoing maintenance requirements and costs associated with different types of generators.
-
Environmental Impact: Consider emissions and fuel efficiency, especially if environmental concerns are a priority.
-
Budget: Balance upfront costs with long-term operating expenses when making a decision.
What are the key features of the Patriot Power Generator?
The Patriot Power Generator is a portable solar generator designed for emergency preparedness and off-grid use. Key features include:
-
Solar Powered: Uses solar panels to generate and store electricity, providing a renewable energy source.
-
Portable Design: Lightweight and compact, making it easy to transport and store.
-
Silent Operation: No engine noise, ideal for quiet environments or stealth power needs.
-
Multiple Outlets: Typically includes various AC and DC outlets to power different devices.
-
Battery Capacity: Often equipped with a lithium-ion battery for efficient energy storage.
-
Expandable: Many models allow for additional solar panels to increase charging capacity.
-
Long Shelf Life: Can be stored for extended periods without losing charge, making it suitable for emergency preparedness.
-
Clean Energy: Produces no emissions during operation, making it environmentally friendly.
| Generator Type | Power Output Range | Typical Applications | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gasoline | 1,000 - 20,000 watts | Home backup, Camping | $300 - $5,000 |
| Diesel | 5,000 - 50,000+ watts | Industrial, Large-scale backup | $5,000 - $50,000+ |
| Natural Gas | 5,000 - 150,000+ watts | Home standby, Commercial | $3,000 - $30,000+ |
| Propane | 1,000 - 30,000 watts | Home backup, RVs | $500 - $15,000 |
| Solar (Portable) | 100 - 3,000 watts | Camping, Small appliances | $200 - $5,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
How can power generators improve energy resilience?
Power generators play a crucial role in enhancing energy resilience for individuals, businesses, and communities. They provide:
-
Emergency Backup: During power outages caused by natural disasters or grid failures, generators ensure critical systems remain operational.
-
Business Continuity: Companies can maintain operations during power interruptions, minimizing financial losses and disruptions.
-
Remote Power: Generators enable electricity access in off-grid locations, supporting construction sites, events, and remote living.
-
Grid Support: Large-scale generators can supplement the power grid during peak demand periods, preventing blackouts.
-
Healthcare Reliability: Hospitals and medical facilities rely on generators to maintain life-support systems and critical equipment during outages.
By providing a reliable alternative power source, generators contribute significantly to overall energy security and resilience, ensuring that essential services and operations can continue even when the main power supply is compromised.
In conclusion, power generators are versatile and essential tools for ensuring a stable electricity supply in various scenarios. From portable solar units for camping to large-scale diesel generators for industrial applications, there’s a generator type suited for nearly every need. By understanding the different types, features, and applications of power generators, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions to enhance their energy resilience and preparedness for various situations.